This years ‘Continuity in Architecture’ field trip took the group to on of the oldest cities in Western Europe, Lisbon, the capital city of Portugal. Sam Stone has spent a good portion of his first semester studies experimenting in the workshop and describes his thought and working process for us.
Whilst visiting the city of Lisbon the notion of it’s craft is almost tangible, from the decorative wrought iron verandas to the tessellated azulejo tiles, the manual, hand made implications of making the city are evident throughout it.What impressed me most was the ostentatious display of skill in the stonemasonry work of the manueline architecture in an area of Lisbon named Belém. It intrigued me to understand the depth of knowledge and skill needed to create such profound displays of craftsmanship.
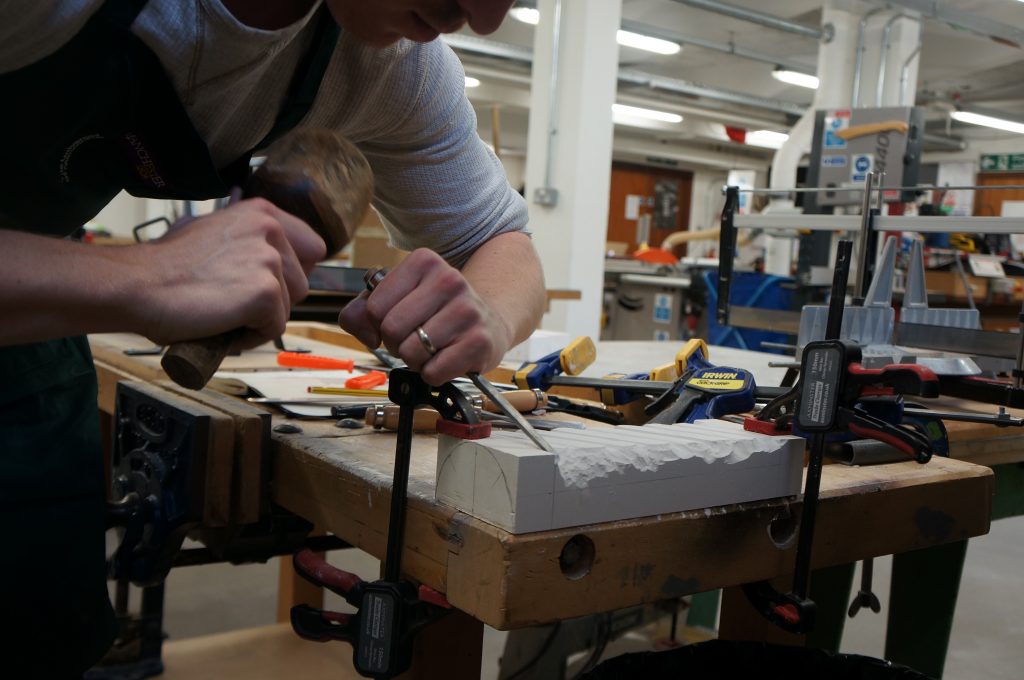

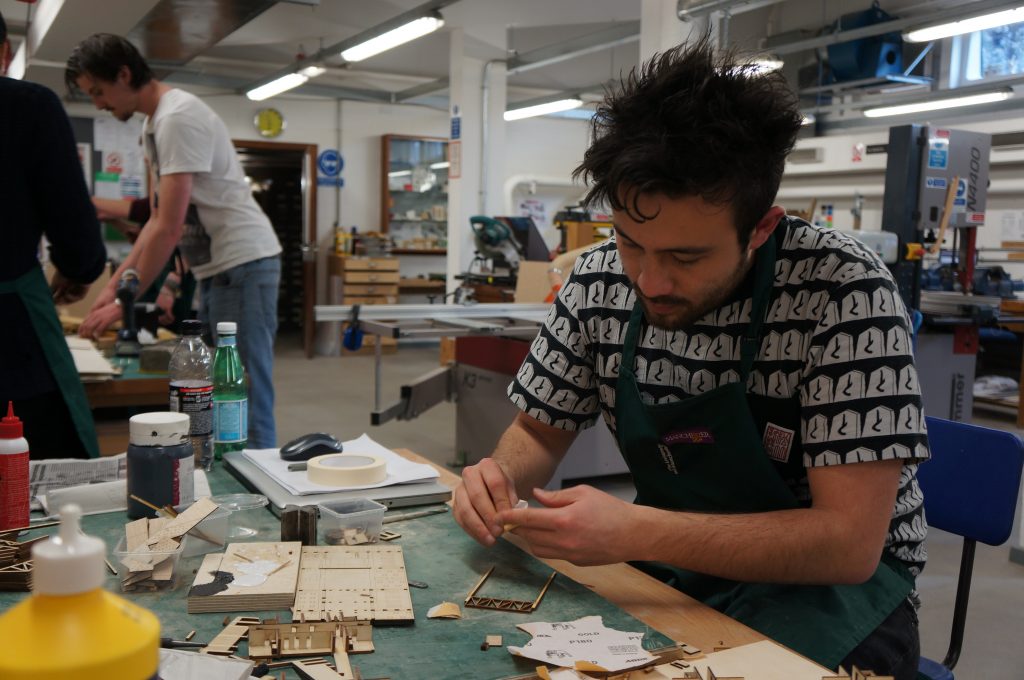
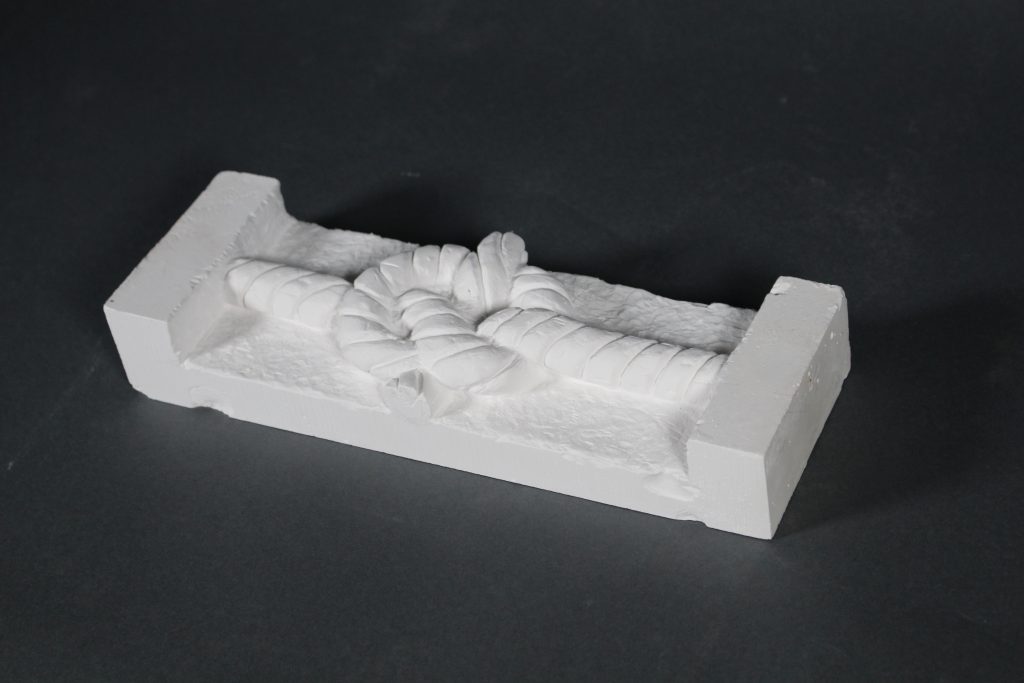
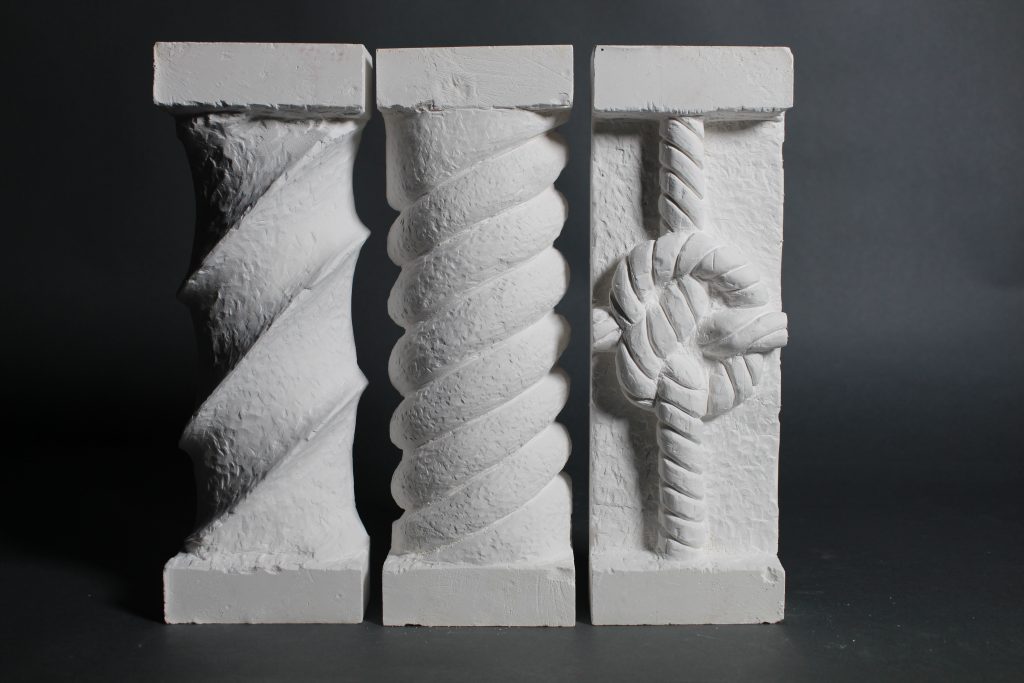
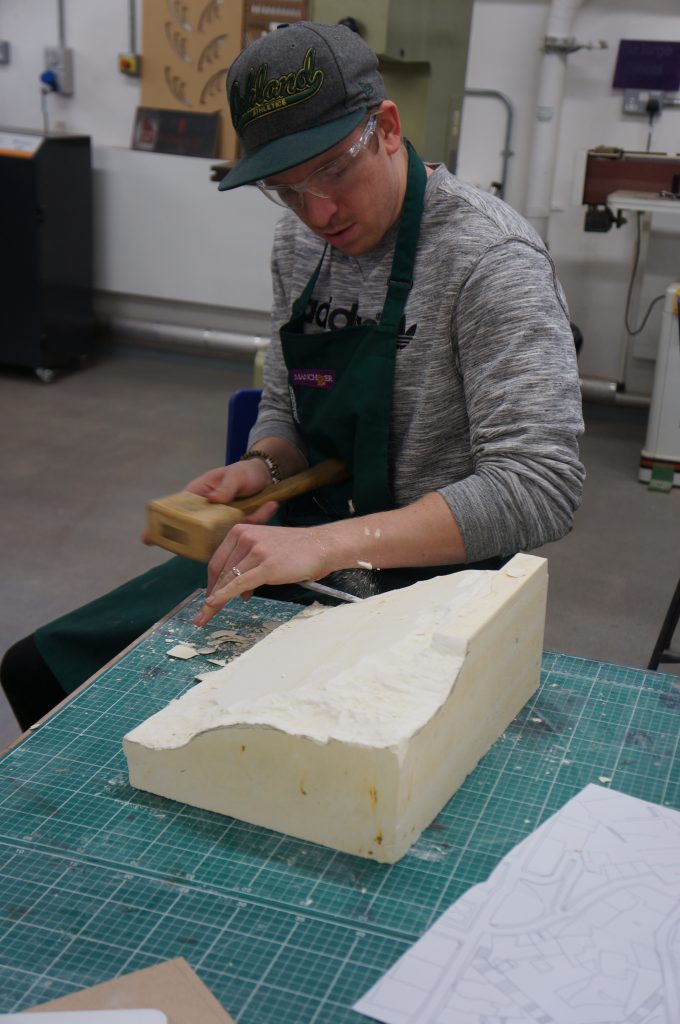
My aim initially was to learn through making, as a direct response to my early research into the various crafts of Lisbon. I started with studies into the processes of stonemasonry (manueline style columns), mimicking the carving and chiseling of stone by using plaster as a more malleable material.Work started off tentatively and without prior experience of carving or sculpting I slowly tapped away at the block removing minimal material. After a while, confidence grew and I became more efficient, quicker and more clinical with my actions. Repetition meant a gradual understanding of the how the material breaks away, how hard to throw the hammer and which way to hold the chisel. What did take me six strikes, now took me one and material would come away precisely where intended, rather than too much or too little.
The resultant studies link back well to my interpretation of Lisbon as a crafted city, and I hope to transfer this knowledge into design/programme at a later stage.
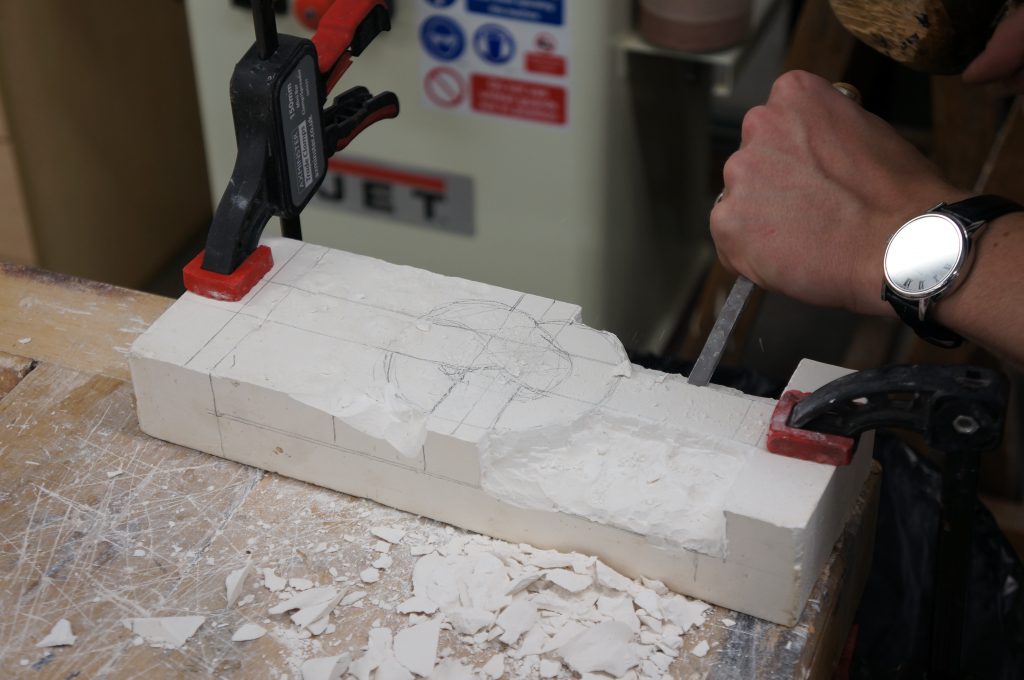

My first three outputs are studies into manueline style architectural elements in stone, each work advancing in difficulty, starting with a simple twisted flute column to a decorative rope knot. I gained a partial understanding of what it means to me to be a craftsman; having a true understanding of material, knowledge and economy of technique and most evidently, much practice and repetition.


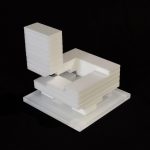
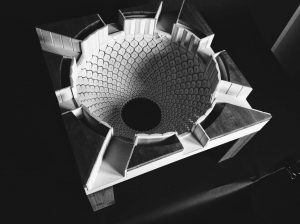
After gaining more confidence with the tools, the material and act of carving, I attempted to produce a concept model and 1:500 site model. I thought these early analytical studies and their method of production, along with site analysis could inform my approach to design later on.
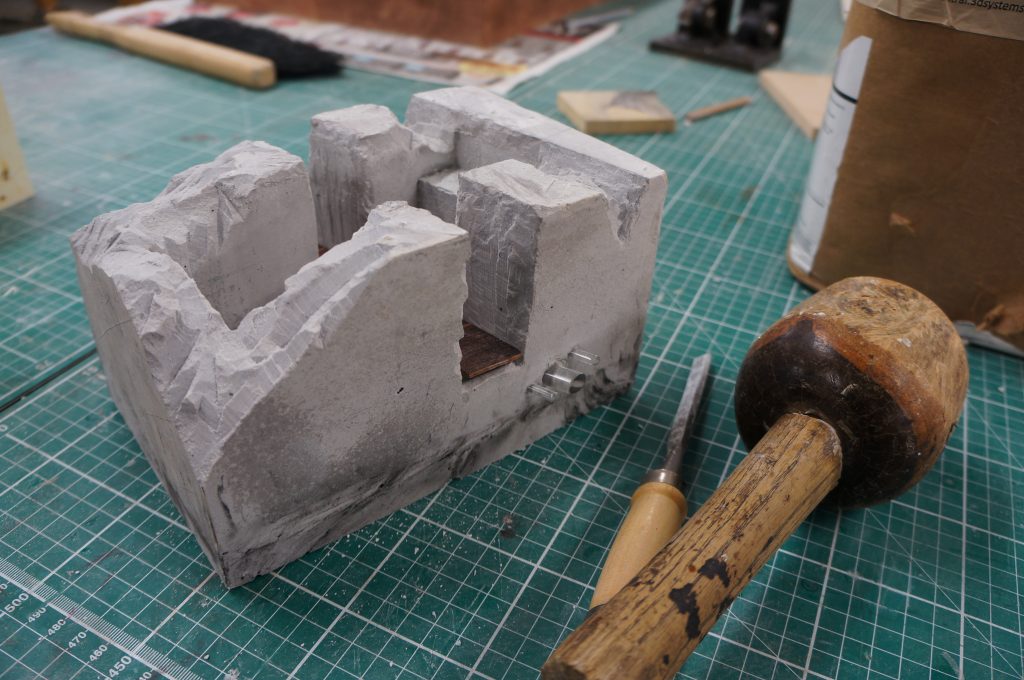

The concept model outlines my approach to design decisions on the site. The block is cast stone plaster with the landscape of the site ‘excavated’ by foam formwork. Protruding perspex rods under the lateral void describe the transient nature of the road that divides both sides of the site. A mahogany piece rests on the stepped landscape as an indicator of ‘place’ I wish to create in the void.

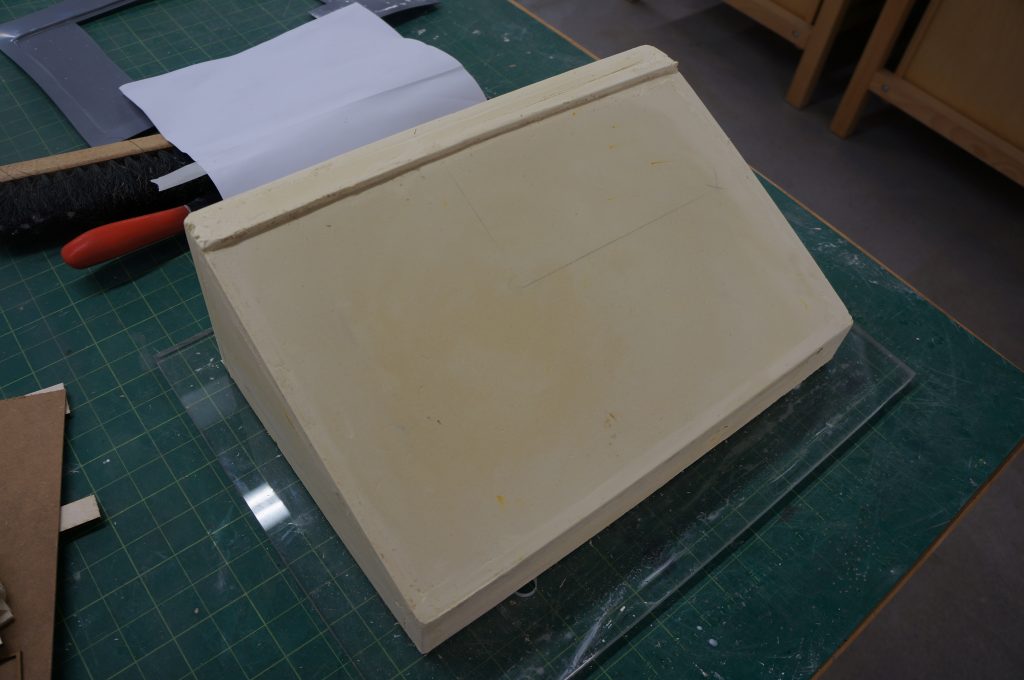
The 1:500 site model was carved out topography from a casted block of pigmented plaster. The excavated, subtracted nature of the landscape suited this method of modelling. Faster methods could include using the CNC machine to mechanically remove material, or making an accurate mold. However, through manually carving away to reveal the site I grasped a deeper understanding of the varied topography and stepped character of the sloped landscape of the site. It also enabled me to interrogate the landscape closer.
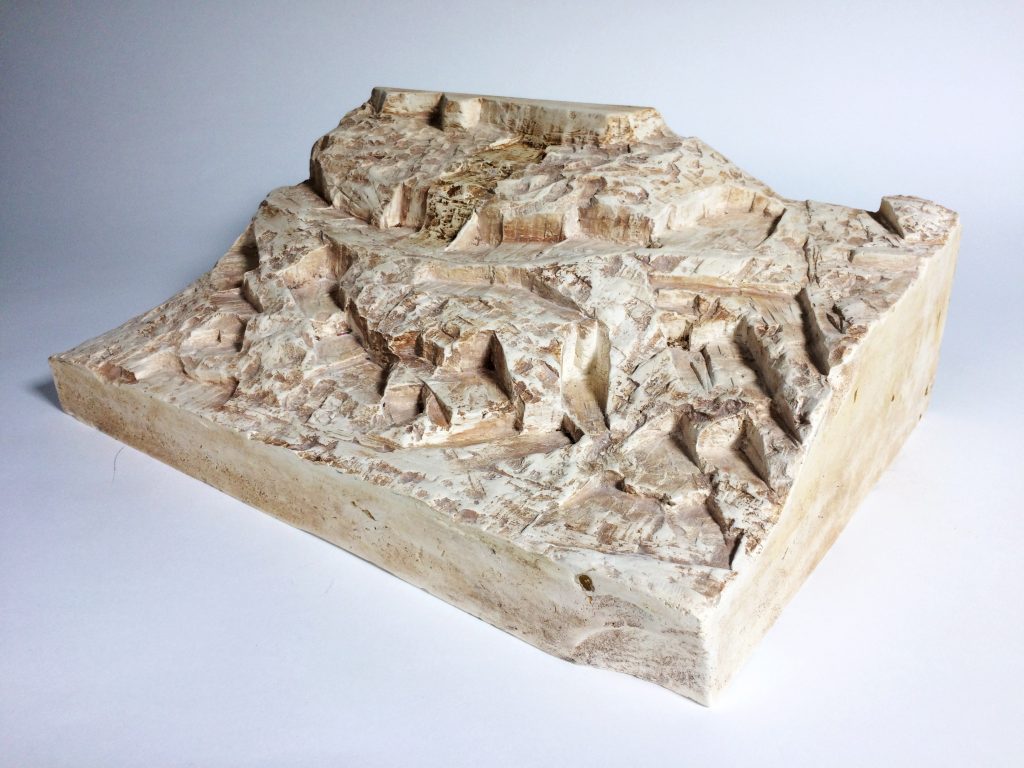



If I was to offer advice to anyone wanting to experiment with modelmaking in a similar way I’d say spend time to learn the particular craft or method, its great to learn a new skill and you could find out something unique about your abilities.
Don’t rush it, at times modelling requires close attention and care, mistakes can be difficult to amend (especially in painted plaster!). As always don’t hurry modelling, if you think the model making method could help inform your design decisions later, it’s worth being patient.
– Sam Stone Jan 2017
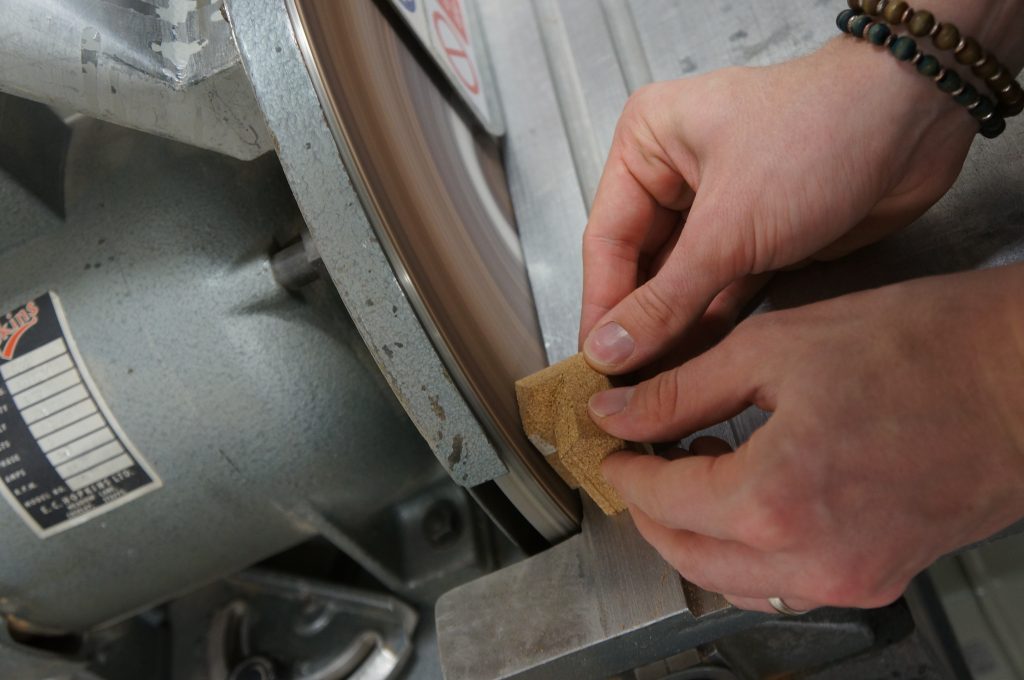
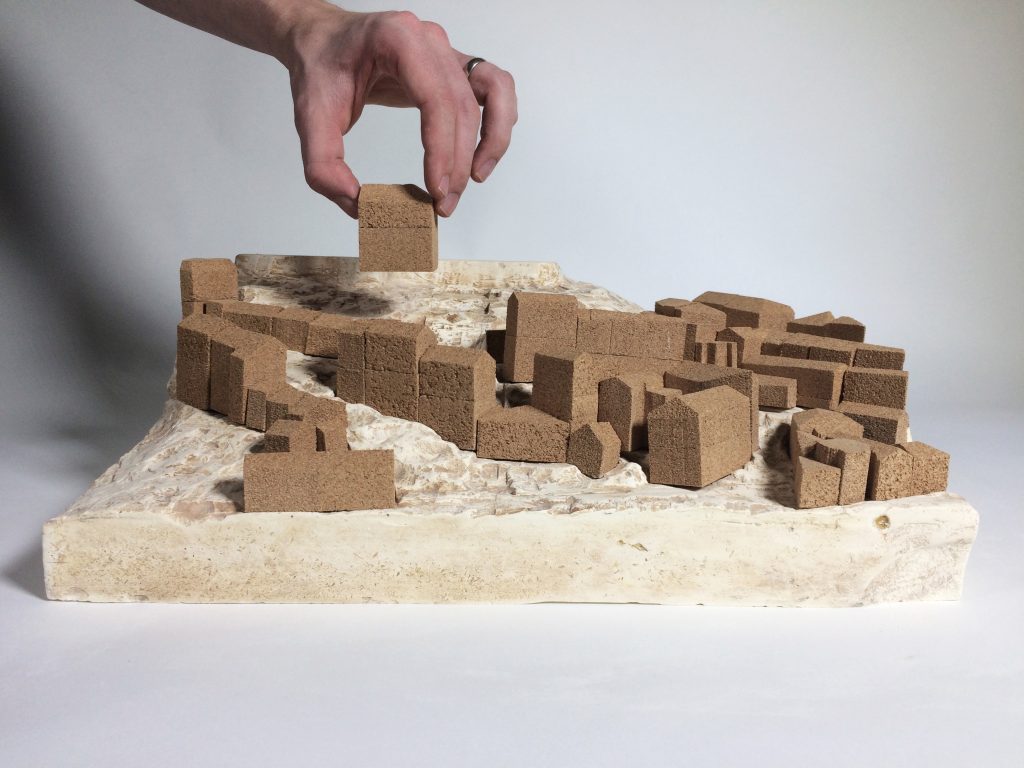


It’s great that Sam decided to approach his studies in this ‘hands on’ way and especially that he took the time to really improve his understanding of the material. The commitment of time is always a big issue to working this way but in marrying his practical trial and error approach to making Sam has been able to balance other study commitments against the making craft he clearly enjoys.
– Scott